CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY IN INDIA
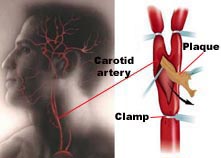
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is a surgical procedure that is performed to remove deposits of fat, called plaque, from the carotid arteries in the neck. These two main arteries, one on each side of the neck, deliver blood and oxygen to the brain. Plaque builds up in large- and medium-sized arteries as people get older, more in some people than others depending on lifestyle and hereditary factors. This build up is a vascular disease called atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries. When this happens in either one or both of the carotid arteries, they can become narrowed, a condition called stenosis. During a carotid endarterectomy, a surgeon removes the fatty deposits to correct the narrowing and to allow blood and oxygen to flow freely to the brain.
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is a surgical procedure used to prevent stroke, by correcting stenosis (narrowing) in the common carotid artery. Endarterectomy is the removal of material on the inside (end-) of an artery.
Atherosclerosis causes plaque to form in the carotid arteries, usually at the fork where the common carotid artery divides into the internal and external carotid artery. The plaque can build up in the inner surface of the artery (lumen), and narrow or constrict the artery. Pieces of the plaque, called emboli, can break off (i.e. embolize) and travel up the internal carotid artery to the brain, where it blocks circulation, and can cause death of the brain tissue.
Diagnosis in India
The presence and degree of stenosis in the carotid artery must be determined before a doctor decides that carotid endarterectomy is necessary. Carotid stenosis can sometimes be detected in a routine checkup, especially when a detailed history reveals to the doctor that the patient has experienced symptoms of TIA or stroke. The doctor will use a stethoscope to listen to blood flow in the carotid artery and may hear an abnormal rushing sound called a “bruit” (pronounced “brew-ee”) that will indicate narrowing in the artery. The absence of sound, however, does not mean there is no risk. More extensive testing will most likely have to be done to determine the degree of stenosis and the potential of risk for the patient.
Preparation in India
If carotid ultrasonography or arteriography procedures were not performed earlier to diagnose carotid stenosis, these tests will be performed before surgery to evaluate the amount of plaque and the extent and location of narrowing in the patient’s carotid arteries. Other blood vessels in the body are also evaluated. If other arteries show significant signs of artherosclerosis or damage, the patient’s risk for surgery may be too great, and the procedure will not be performed. Aspirin therapy or other clot-prevention medication may be prescribed before surgery. Any underlying medical condition such as high blood pressure or heart disease will be treated prior to carotid endarterectomy to help achieve the best result from the surgery. Upon admission to the hospital , routine blood and urine tests will be performed.
During carotid endarterectomy : -
- You will probably receive general anesthesia. This will make you unconscious and unable to feel pain. Some hospitals may use local anesthesia instead. With local anesthesia, only the part of your body being worked on will be made numb with medicine so that you will not feel pain.
- You will lie on your back on a padded operating table with your head turned to one side. The side that will face up is the side your blocked carotid artery is on.
- Your surgeon will make an incision (a cut) on your neck over your carotid artery. Your surgeon will put a catheter (a flexible tube) in place. Blood will flow through the catheter around the blocked area during surgery.
- Then your surgeon will open your carotid artery. The surgeon will then remove the plaque inside your artery.
- Your artery will be closed up with stitches after the plaque is removed. Blood will now flow through the artery to your brain.
- Your heart and brain activity will be monitored closely during your surgery.
The procedure cannot be performed in case of : -
- Complete internal carotid artery obstruction (because the intraluminal thrombus then extends too far downstream, well into the intracranial portion of the artery, for endarterectomy to be successful).
- Previous stroke on the ipsilateral side with heavy sequelae because there is no point in preventing what has already happened.
- Patient deemed unfit for the operation by the anaesthesiologist.