- Home
- About Us
- Treatment
-
- Hospital
-
- Doctors
- Testimonial
- Cost
- Advanced Fertility
- Contacts
- AMRI Hospital Kolkata
- Ivf Cost in Bangalore
- Back Pain Spine Surgery and Cost in india
- affiliated hospitals centres
- Adjuvant Radiation Therapy in India
- Azoospermia Treatment and Cost in India
- Balloon Microdecompression Treatment and Cost in india
- Asd Closure Device Surgery Cost in India
Cerebral Angioplasty in India: Advanced Stroke Prevention & Treatment
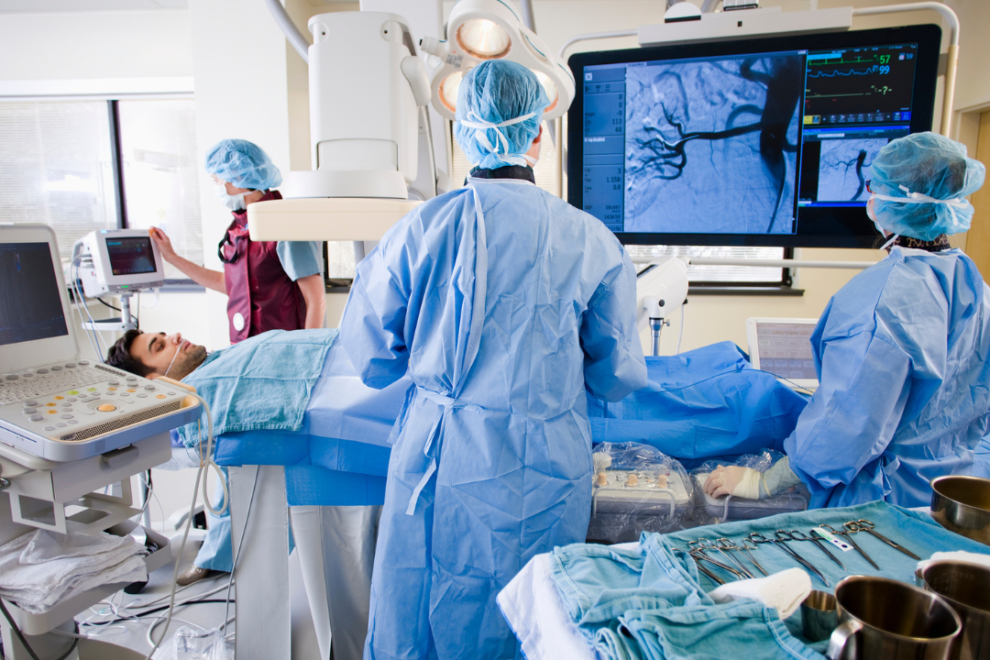
Typically a catheter is inserted into a large artery (such as the femoral artery) and threaded through the circulatory system to the carotid artery, where a contrast agent is injected. A series of radiographs is taken as the contrast agent spreads through the brain's arterial system, then a second series as it reaches the venous system.
This is often the treatment choice if you've had several small strokes that can't be treated with medication.

Emergency Cases
The surgeon inserts a small balloon into one of the blood vessels supplying the brain. The balloon enlarges the vessel and increases blood flow.
Cerebral angiography is done in the hospital or large radiology center. You will be asked to lie on an x-ray table. Your head is positioned and held still using a strap, tape, or sandbags, so you do not move during the procedure. The health care provider will attach electrocardiogram (ECG) leads to your arms and legs, which monitor your heart activity during the test.
Before the test starts, you will be given a mild sedative to help you relax.
An area of your body, usually the groin, is cleaned and numbed with a local numbing medicine (anesthetic). A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is placed through an artery and carefully moved up through the main blood vessels in the belly area and chest and into an artery in the neck. Moving x-ray images help the doctor position the catheter.
Once the catheter is in place, a special dye (contrast material) is injected into catheter. X-ray images are taken to see how the dye moves through the artery and blood vessels of the brain. The dye helps highlight any blockages in blood flow.
Wish to know our Neurosurgery skills, send us your message Or email at [email protected] / Call +91 9029304141
After the x-rays are taken, the needle and catheter are withdrawn. Pressure is immediately applied on the leg at the site of insertion for 10 – 15 minutes to stop the bleeding. After that time, the area is checked and a tight bandage is applied. Your leg should be kept straight for 12 hours after the procedure.
Digital subtraction angiography (DSI) uses a computer to “subtract” or take out the bones and tissues in the area viewed, so that only the blood vessels filled with the contrast dye are seen.
Although angioplasty with stent placement is theoretically applicable to the treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis, the safety and efficacy of this modality are controversial. In 2002. At that time, evaluation of this method was limited to several small retrospective series in which varying complication rates were demonstrated. Additionally, these studies largely focused on posterior circulation atherosclerosis and lacked data regarding stenosis of the anterior circulation, including the ICA. Recently, a handful of studies have emerged that allow for a more complete assessment of endovascular stent treatment and reveal developments in this rapidly changing field.
Read Also :-
- Cancer Treatment in India: Advanced Care and Affordable Solutions
- Advanced Cancer Surgery in India | Leading Oncologists & World-Class Care
- Sigmoidoscopy Surgery in India: Early Detection and Affordable Care for Colon Health
- Breast Implants in India: Safe and Affordable Enhancement Options
- Carotid Endarterectomy in India: Advanced Stroke Prevention Surgery
- Carotid Artery Disease Surgery in India: Prevent Strokes with Advanced Care
Committed To Build Positive, Safe, Patient Focused Culture.
High Quality
Care
Home Review
Medicine
All Advanced
Equipment
Book An Appointment

At We Care India, we offer complete medical services for your entire family, from routine check-ups to injury care, ensuring personalized attention and expert assistance for all your health needs.
More Treatments
Book An Appointment
Phone
+91 9029304141
Our Locations in India
Delhi
Mumbai
Bangalore
Chennai
Hyderabad


